[!NOTE]
该功能在 EF Core 8.0 中被添加。
Azure SQL 和 SQL Server 拥有一种特殊数据类型称为 hierarchyid,用于存储层次化数据。在这种情况下,“层次化数据”基本上指的是形成树状结构的数据,其中每个项目都可以有父级和/或子级。这类数据的例子包括:
- 一个组织结构
- 文件系统
- 项目中的一组任务
- 语言术语的分类
- 网页之间链接的图形
然后,数据库能够使用这些数据的层次化结构来运行查询。例如,查询可以查找给定项目的祖先和依赖项,或找到层次结构中某个深度的所有项目。
在 .NET 和 EF Core 中使用 HierarchyId
在最低层面,Microsoft.SqlServer.Types NuGet 包包括一个称为 SqlHierarchyId 的类型。虽然这个类型支持处理 hierarchyid 值,但在 LINQ 中使用它有些复杂。
在下一个层次上,一个新的 Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Abstractions 包被引入,其中包含了一个用于实体类型的更高级别的 HierarchyId 类型。
[!TIP]
HierarchyId类型更接近 .NET 的惯例,而不是像SqlHierarchyId那样基于 .NET Framework 类型在 SQL Server 数据库引擎中的托管方式。HierarchyId旨在与 EF Core 一起工作,但它也可以在 EF Core 之外的其他应用程序中使用。Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Abstractions包不引用任何其他包,并因此对部署应用程序大小和依赖项的影响最小。
使用 HierarchyId 对于 EF Core 功能如查询和更新需要 Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.HierarchyId 包。这个包引入了 Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.Abstractions 和 Microsoft.SqlServer.Types 作为传递依赖项,因此通常是唯一需要的包。
.NET Core CLI
dotnet add package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.HierarchyIdVisual Studio
-
工具 > NuGet 包管理器 > 包管理器控制台
-
运行以下命令:
Install-Package Microsoft.EntityFrameworkCore.SqlServer.HierarchyId
提示:您也可以通过右击项目并选择 管理 NuGet 包 来安装包
安装包后,通过在应用程序调用 UseSqlServer 时调用 UseHierarchyId 来启用 HierarchyId 的使用。例如:
options.UseSqlServer(
connectionString,
x => x.UseHierarchyId());建模层次结构
HierarchyId 类型可以用于实体类型的属性。例如,假设我们想模拟一些虚构哈比人的父系家谱树。在 Halfling 实体类型中,可以使用 HierarchyId 属性来定位家谱树中的每个哈比人。
public class Halfling
{
public Halfling(HierarchyId pathFromPatriarch, string name, int? yearOfBirth = null)
{
PathFromPatriarch = pathFromPatriarch;
Name = name;
YearOfBirth = yearOfBirth;
}
public int Id { get; private set; }
public HierarchyId PathFromPatriarch { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public int? YearOfBirth { get; set; }
}[!TIP]
这里和下面的例子中显示的代码来自 HierarchyIdSample.cs。
[!TIP]
如果需要,
HierarchyId适用于作为键属性类型。
在这个例子中,家谱树以家族的族长为根。每个哈比人都可以使用其 PathFromPatriarch 属性从族长沿树向下追溯。SQL Server 使用这些路径的紧凑二进制格式,但在处理代码时,通常会解析为人类可读的字符串表示形式。在这种表示中,每一级的位置由 / 字符分隔。例如,考虑下面图表中的家谱树:
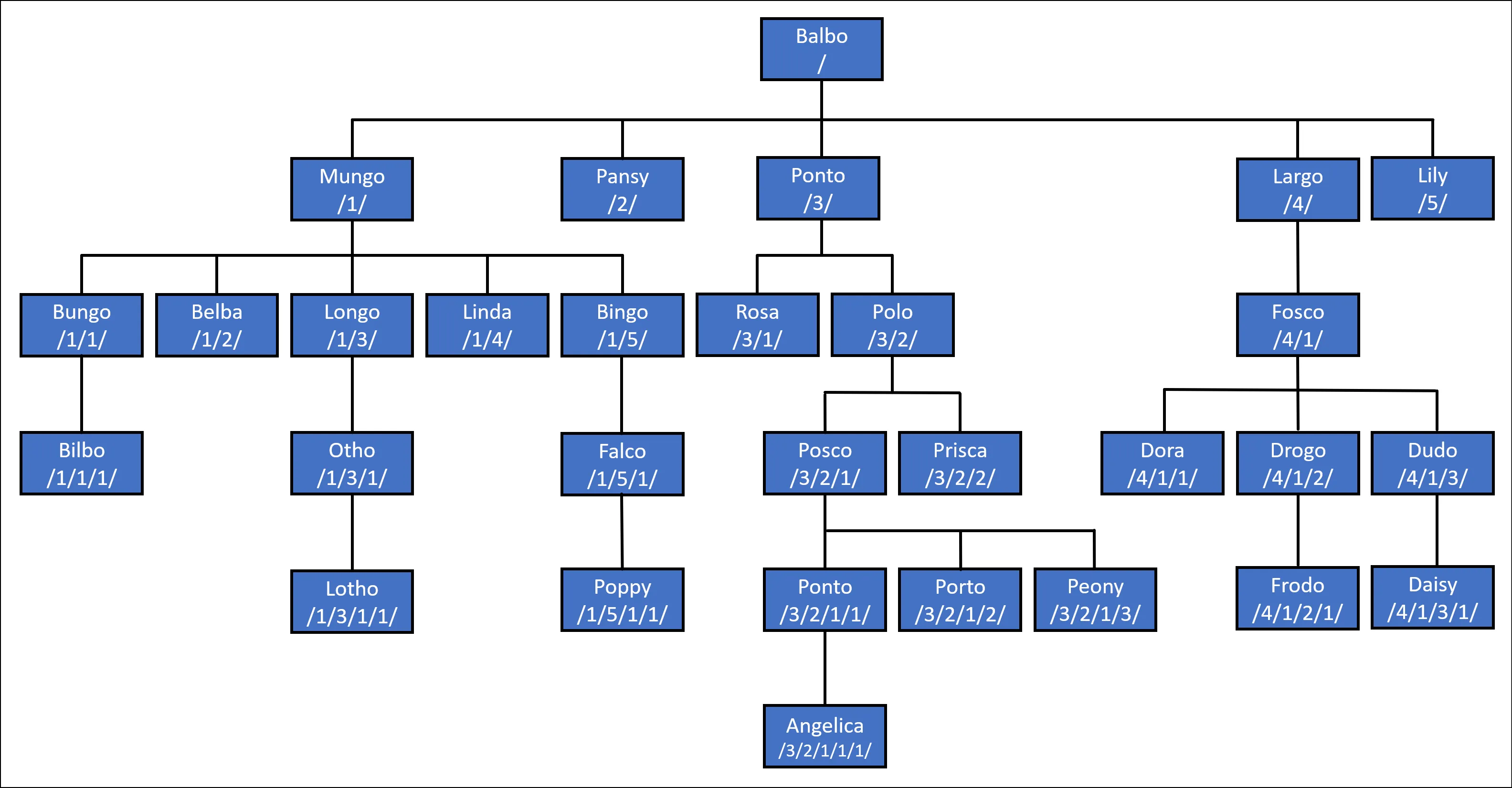
在这棵树中:
- Balbo 在树根处,表示为
/。 - Balbo 有五个子女,分别表示为
/1/、/2/、/3/、/4/和/5/。 - Balbo 的第一个孩子,Mungo,也有五个子女,分别表示为
/1/1/、/1/2/、/1/3/、/1/4/和/1/5/。注意 Balbo(/1/)的HierarchyId是他所有孩子的前缀。 - 类似地,Balbo 的第三个孩子,Ponto,有两个孩子,分别表示为
/3/1/和/3/2/。再次说明,这些孩子中的每一个都由 Ponto 的HierarchyId作为前缀,表示为/3/。 - 依此类推,沿着树向下…
以下代码将这个家谱树插入到数据库中使用 EF Core:
await AddRangeAsync(
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/"), "Balbo", 1167),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/"), "Mungo", 1207),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/2/"), "Pansy", 1212),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/"), "Ponto", 1216),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/"), "Largo", 1220),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/5/"), "Lily", 1222),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/1/"), "Bungo", 1246),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/2/"), "Belba", 1256),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/3/"), "Longo", 1260),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/4/"), "Linda", 1262),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/5/"), "Bingo", 1264),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/1/"), "Rosa", 1256),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/"), "Polo"),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/"), "Fosco", 1264),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/1/1/"), "Bilbo", 1290),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/3/1/"), "Otho", 1310),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/5/1/"), "Falco", 1303),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/1/"), "Posco", 1302),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/2/"), "Prisca", 1306),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/1/"), "Dora", 1302),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/2/"), "Drogo", 1308),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/3/"), "Dudo", 1311),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/3/1/1/"), "Lotho", 1310),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/1/5/1/1/"), "Poppy", 1344),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/1/1/"), "Ponto", 1346),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/1/2/"), "Porto", 1348),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/1/3/"), "Peony", 1350),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/2/1/"), "Frodo", 1368),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/4/1/3/1/"), "Daisy", 1350),
new Halfling(HierarchyId.Parse("/3/2/1/1/1/"), "Angelica", 1381));
await SaveChangesAsync();[!TIP]
如果需要,可以使用小数值在两个现有节点之间创建新节点。例如,
/3/2.5/2/位于/3/2/2/和/3/3/2/之间。
查询层次结构
HierarchyId 公开了几个可以在 LINQ 查询中使用的方法。
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
GetAncestor(int n) | 获取一棵树中 n 级别向上的节点。 |
GetDescendant(HierarchyId? child1, HierarchyId? child2) | 获得一个大于 child1 小于 child2 的后代节点的值。 |
GetLevel() | 获取此节点在层次化树中的级别。 |
GetReparentedValue(HierarchyId? oldRoot, HierarchyId? newRoot) | 获取表示新节点的值,该节点从 newRoot 到这个节点的路径与从 oldRoot 到这个节点的路径相等,有效地将这个节点移动到新位置。 |
IsDescendantOf(HierarchyId? parent) | 获取一个值,指示此节点是否是 parent 的后代。 |
此外,运算符 ==、!=、<、<=、> 和 >= 可用。
以下是在 LINQ 查询中使用这些方法的示例。
在树中获取给定级别的实体
以下查询使用 GetLevel 返回家庭树中给定级别的所有哈比人:
var generation = await context.Halflings.Where(halfling => halfling.PathFromPatriarch.GetLevel() == level).ToListAsync();这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE [h].[PathFromPatriarch].GetLevel() = @__level_0在循环中运行这段代码,我们可以获得每一代的哈比人:
Generation 0: Balbo
Generation 1: Mungo, Pansy, Ponto, Largo, Lily
Generation 2: Bungo, Belba, Longo, Linda, Bingo, Rosa, Polo, Fosco
Generation 3: Bilbo, Otho, Falco, Posco, Prisca, Dora, Drogo, Dudo
Generation 4: Lotho, Poppy, Ponto, Porto, Peony, Frodo, Daisy
Generation 5: Angelica获取实体的直接祖先
以下查询使用 GetAncestor 根据哈比人的名称找到直接祖先:
async Task<Halfling?> FindDirectAncestor(string name)
=> await context.Halflings
.SingleOrDefaultAsync(
ancestor => ancestor.PathFromPatriarch == context.Halflings
.Single(descendent => descendent.Name == name).PathFromPatriarch
.GetAncestor(1));这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT TOP(2) [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE [h].[PathFromPatriarch] = (
SELECT TOP(1) [h0].[PathFromPatriarch]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h0]
WHERE [h0].[Name] = @__name_0).GetAncestor(1)对 “Bilbo” 运行此查询返回 “Bungo”。
获取实体的直接后代
以下查询也使用 GetAncestor,但这次是找到给定哈比人名称的直接后代:
IQueryable<Halfling> FindDirectDescendents(string name)
=> context.Halflings.Where(
descendent => descendent.PathFromPatriarch.GetAncestor(1) == context.Halflings
.Single(ancestor => ancestor.Name == name).PathFromPatriarch);这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE [h].[PathFromPatriarch].GetAncestor(1) = (
SELECT TOP(1) [h0].[PathFromPatriarch]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h0]
WHERE [h0].[Name] = @__name_0)对 “Mungo” 运行此查询返回 “Bungo”, “Belba”, “Longo”, 和 “Linda”。
获取实体的所有祖先
GetAncestor 用于向上或向下搜索一个级别,或确切地说,指定数量的级别。另一方面,IsDescendantOf 用于找到所有祖先或依赖项。例如,以下查询使用 IsDescendantOf 根据哈比人的名称找到所有祖先:
IQueryable<Halfling> FindAllAncestors(string name)
=> context.Halflings.Where(
ancestor => context.Halflings
.Single(
descendent =>
descendent.Name == name
&& ancestor.Id != descendent.Id)
.PathFromPatriarch.IsDescendantOf(ancestor.PathFromPatriarch))
.OrderByDescending(ancestor => ancestor.PathFromPatriarch.GetLevel());[!IMPORTANT]
IsDescendantOf对其自身返回 true,这就是为什么在上面的查询中将其过滤掉的原因。
这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE (
SELECT TOP(1) [h0].[PathFromPatriarch]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h0]
WHERE [h0].[Name] = @__name_0 AND [h].[Id] <> [h0].[Id]).IsDescendantOf([h].[PathFromPatriarch]) = CAST(1 AS bit)
ORDER BY [h].[PathFromPatriarch].GetLevel() DESC对 “Bilbo” 运行此查询返回 “Bungo”, “Mungo”, 和 “Balbo”。
获取实体的所有后代
以下查询也使用 IsDescendantOf,但这次是返回给定哈比人名称的所有后代:
IQueryable<Halfling> FindAllDescendents(string name)
=> context.Halflings.Where(
descendent => descendent.PathFromPatriarch.IsDescendantOf(
context.Halflings
.Single(
ancestor =>
ancestor.Name == name
&& descendent.Id != ancestor.Id)
.PathFromPatriarch))
.OrderBy(descendent => descendent.PathFromPatriarch.GetLevel());这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE [h].[PathFromPatriarch].IsDescendantOf((
SELECT TOP(1) [h0].[PathFromPatriarch]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h0]
WHERE [h0].[Name] = @__name_0 AND [h].[Id] <> [h0].[Id])) = CAST(1 AS bit)
ORDER BY [h].[PathFromPatriarch].GetLevel()对 “Mungo” 运行此查询返回 “Bungo”, “Belba”, “Longo”, “Linda”, “Bingo”, “Bilbo”, “Otho”, “Falco”, “Lotho”, 和 “Poppy”。
寻找共同祖先
关于这个特定家谱树最常被问到的问题之一是,“Frodo 和 Bilbo 的共同祖先是谁?”我们可以使用 IsDescendantOf 写出这样的查询:
async Task<Halfling?> FindCommonAncestor(Halfling first, Halfling second)
=> await context.Halflings
.Where(
ancestor => first.PathFromPatriarch.IsDescendantOf(ancestor.PathFromPatriarch)
&& second.PathFromPatriarch.IsDescendantOf(ancestor.PathFromPatriarch))
.OrderByDescending(ancestor => ancestor.PathFromPatriarch.GetLevel())
.FirstOrDefaultAsync();这转换为以下 SQL:
SELECT TOP(1) [h].[Id], [h].[Name], [h].[PathFromPatriarch], [h].[YearOfBirth]
FROM [Halflings] AS [h]
WHERE @__first_PathFromPatriarch_0.IsDescendantOf([h].[PathFromPatriarch]) = CAST(1 AS bit)
AND @__second_PathFromPatriarch_1.IsDescendantOf([h].[PathFromPatriarch]) = CAST(1 AS bit)
ORDER BY [h].[PathFromPatriarch].GetLevel() DESC使用 “Bilbo” 和 “Frodo” 运行此查询告诉我们他们的共同祖先是 “Balbo”。
更新层次结构
可以使用正常的 变更跟踪 和 SaveChanges 机制来更新 hierarchyid 列。
重新父级化子层次结构
例如,我相信我们都记得 SR 1752 年的丑闻(又名“LongoGate”),当时 DNA 测试显示 Longo 实际上不是 Mungo 的儿子,而是 Ponto 的儿子!这个丑闻的一个后果是家谱树需要被重写。特别是,Longo 和他所有的后代需要从 Mungo 重新父级化到 Ponto。GetReparentedValue 可以用来做这个。例如,首先查询“Longo”和所有他的后代:
var longoAndDescendents = await context.Halflings.Where(
descendent => descendent.PathFromPatriarch.IsDescendantOf(
context.Halflings.Single(ancestor => ancestor.Name == "Longo").PathFromPatriarch))
.ToListAsync();然后使用 GetReparentedValue 更新 Longo 和每个后代的 HierarchyId,接着调用 SaveChangesAsync:
foreach (var descendent in longoAndDescendents)
{
descendent.PathFromPatriarch
= descendent.PathFromPatriarch.GetReparentedValue(
mungo.PathFromPatriarch, ponto.PathFromPatriarch)!;
}
await context.SaveChangesAsync();这导致以下数据库更新:
SET NOCOUNT ON;
UPDATE [Halflings] SET [PathFromPatriarch] = @p0
OUTPUT 1
WHERE [Id] = @p1;
UPDATE [Halflings] SET [PathFromPatriarch] = @p2
OUTPUT 1
WHERE [Id] = @p3;
UPDATE [Halflings] SET [PathFromPatriarch] = @p4
OUTPUT 1
WHERE [Id] = @p5;使用以下参数:
@p1='9',
@p0='0x7BC0' (Nullable = false) (Size = 2) (DbType = Object),
@p3='16',
@p2='0x7BD6' (Nullable = false) (Size = 2) (DbType = Object),
@p5='23',
@p4='0x7BD6B0' (Nullable = false) (Size = 3) (DbType = Object)[!NOTE]
HierarchyId属性的参数值会以它们的紧凑二进制格式发送到数据库。
更新之后,查询 “Mungo” 的后代会返回 “Bungo”、“Belba”、“Linda”、“Bingo”、“Bilbo”、“Falco” 和 “Poppy”,而查询 “Ponto” 的后代会返回 “Longo”、“Rosa”、“Polo”、“Otho”、“Posco”、“Prisca”、“Lotho”、“Ponto”、“Porto”、“Peony” 和 “Angelica”。
函数映射
| .NET | SQL |
|---|---|
| hierarchyId.GetAncestor(n) | @hierarchyId.GetAncestor(@n) |
| hierarchyId.GetDescendant(child) | @hierarchyId.GetDescendant(@child, NULL) |
| hierarchyId.GetDescendant(child1, child2) | @hierarchyId.GetDescendant(@child1, @child2) |
| hierarchyId.GetLevel() | @hierarchyId.GetLevel() |
| hierarchyId.GetReparentedValue(oldRoot, newRoot) | @hierarchyId.GetReparentedValue(@oldRoot, @newRoot) |
| HierarchyId.GetRoot() | hierarchyid::GetRoot() |
| hierarchyId.IsDescendantOf(parent) | @hierarchyId.IsDescendantOf(@parent) |
| HierarchyId.Parse(input) | hierarchyid::Parse(@input) |
| hierarchyId.ToString() | @hierarchyId.ToString() |