深入解析MediatR通知发布机制:挑战与解决方案 🚀
为什么MediatR通知发布会阻塞你的应用?
在现代软件开发中,异步处理成为提升系统响应能力和扩展性的重要手段。然而,MediatR的通知发布机制却因为其阻塞特性让许多开发者感到头疼。虽然它支持简单的进程内发布/订阅,但实际上却不是异步的。本文将深入探讨这一问题,并通过分布式追踪工具OpenTelemetry来分析其性能表现。
MediatR通知发布器如何运作?
MediatR提供了两个内置的INotificationPublisher接口实现:ForeachAwaitPublisher和TaskWhenAllPublisher。两者都会阻塞发布线程,直到所有处理器完成。以下是接口定义及两个实现:
public interface INotificationPublisher
{
Task Publish(
IEnumerable<NotificationHandlerExecutor> handlerExecutors,
INotification notification,
CancellationToken cancellationToken);
}ForeachAwaitPublisher
顺序执行各个处理器,确保执行顺序可预测:
public class ForeachAwaitPublisher : INotificationPublisher
{
public async Task Publish(
IEnumerable<NotificationHandlerExecutor> handlerExecutors,
INotification notification,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
foreach (var handler in handlerExecutors)
{
await handler.HandlerCallback(notification, cancellationToken).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
}
}TaskWhenAllPublisher
提供并发执行处理器的能力,但仍需等待所有处理器完成:
public class TaskWhenAllPublisher : INotificationPublisher
{
public Task Publish(
IEnumerable<NotificationHandlerExecutor> handlerExecutors,
INotification notification,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
var tasks = handlerExecutors
.Select(handler => handler.HandlerCallback(notification, cancellationToken))
.ToArray();
return Task.WhenAll(tasks);
}
}使用OpenTelemetry验证阻塞特性
通过设置一个简单的例子并使用OpenTelemetry追踪,我们可以清楚地看到这些发布器如何阻塞请求线程。
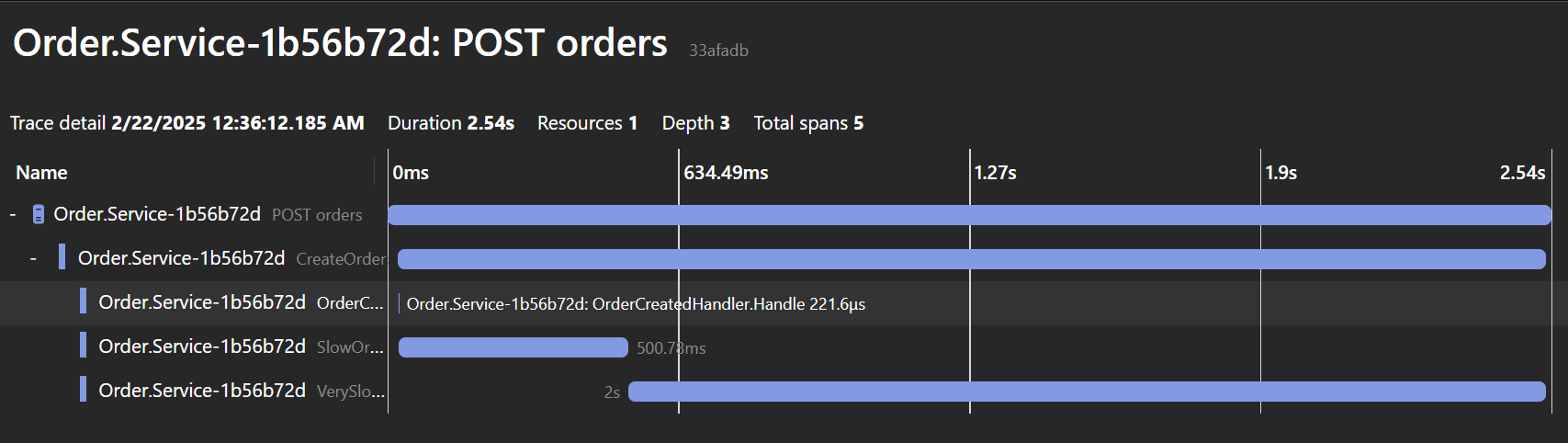
如何实现真正的异步通知发布?
为了解决上述问题,我们可以使用System.Threading.Channels实现一个自定义的通知发布器,使得发布线程能够立即返回,而非等待处理器完成。
public class ChannelPublisher(NotificationsQueue queue) : INotificationPublisher
{
public async Task Publish(
IEnumerable<NotificationHandlerExecutor> handlerExecutors,
INotification notification,
CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
await queue.Writer.WriteAsync(
new NotificationEntry(handlerExecutors.ToArray(), notification),
cancellationToken);
}
}背景服务负责处理队列中的通知:
public class ChannelPublisherWorker(NotificationsQueue queue) : BackgroundService
{
protected override async Task ExecuteAsync(CancellationToken stoppingToken)
{
await foreach (NotificationEntry entry in queue.Reader.ReadAllAsync(stoppingToken))
{
await Parallel.ForEachAsync(entry.Handlers, stoppingToken, async (executor, token) =>
{
await executor.HandlerCallback(entry.Notification, token);
});
}
}
}对比不同方法的性能表现 🔍
使用OpenTelemetry分析ChannelPublisher实现,我们发现HTTP请求迅速完成,而处理器的执行则作为独立的追踪记录出现,显著提高系统响应能力。
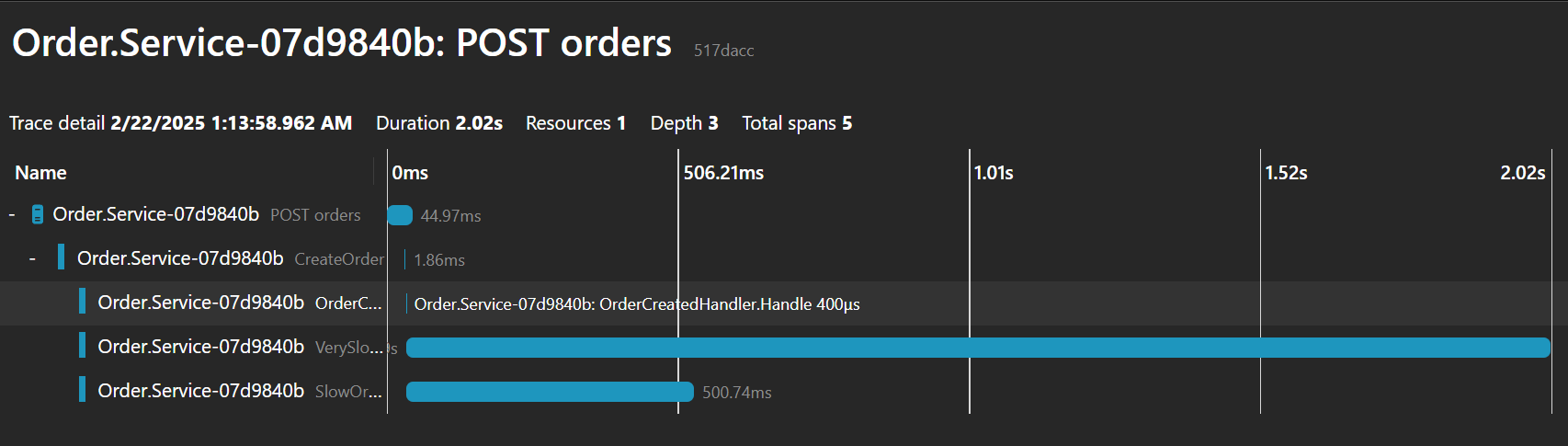
是否值得采用这种方法?
虽然ChannelPublisher提供了异步处理能力,但它也增加了额外复杂性,如错误处理、消息持久性等。在复杂场景中,使用消息队列系统(如RabbitMQ或Amazon SQS)可能更加合适。
如果你正在寻找一种提升系统性能的方法,不妨尝试以上方案,并根据实际需求选择合适的技术架构。希望本文对你的开发工作有所帮助!